In the process of using cell culture consumables such as cell factories to cultivate cells, what we are most afraid of encountering is the situation where the cells will be polluted. In order to avoid contamination when using cell culture consumables such as cell factories to cultivate cells , it is necessary to have a certain understanding of possible pollution, which is mainly divided into chemical pollution and biological pollution:
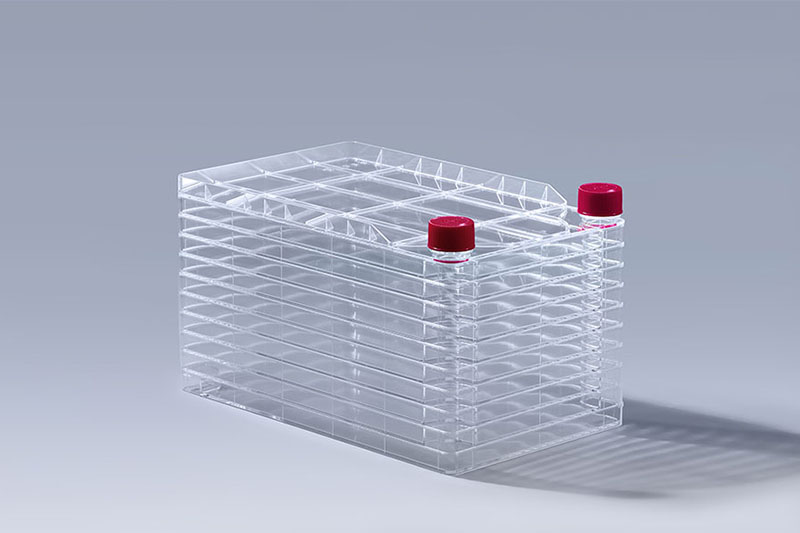
FuDau 10-Layers-Cell-Factory
Chemical contamination in cell culture consumables such as cell factories
Chemical pollution is some pollution methods that can stimulate the cell culture process, mainly toxic and irritating chemicals to cells. This type of pollution is mainly the equipment pollution that occurs in our cell factory and other cell culture consumables.
Bacterial endotoxins are more noticeable in chemical pollution. It is a hydrophobic cell wall component released by the disintegration of Gram-negative bacterial cells after death, and has a strong adsorption capacity for plastics and other highly hydrophobic substances. Bacterial endotoxins can stimulate some cells to produce some hormones or cytokines, which can affect the growth and experimental results of cultured cells in cell culture consumables such as cell factories. Bacterial endotoxin is the most important clinical pyrogen (that is, injection into animals will cause fever in animals), so vaccines and cytokines produced by cell culture are used in the production of clinical drugs to avoid bacteria Endotoxin contamination.
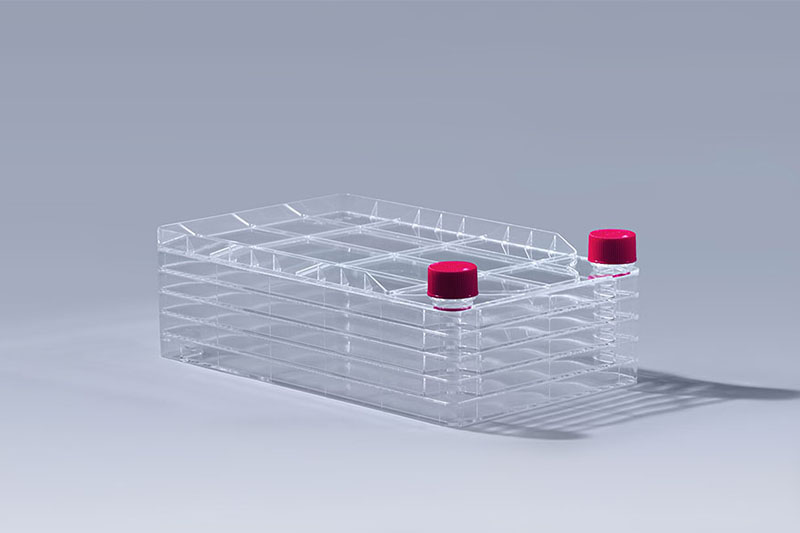
FuDau 5-Layers-Cell-Factory
Biological contamination in cell culture consumables such as cell factories
There are many types of biological pollution, such as bacteria, mold and yeast pollution that we can easily find, and virus pollution, mycoplasma pollution and other cell pollution that are relatively difficult to find.
Bacteria, mold and yeast contamination are relatively easy to find because they have strong living conditions and can grow rapidly in a suitable environment. These contaminations are relatively easy to observe. When they are contaminated, they will cause the culture fluid in the cell factory to appear turbid, or they can be seen through microscope observation.
Since the virus has species specificity, the probability of virus contamination is relatively small. However, it is difficult to find that the cells cultured by cell culture consumables such as cell factories are contaminated by viruses, because the virus particles are extremely small, and ordinary laboratories are not able to detect the viruses contaminated in cell culture. Because viruses generally lie dormant inside cells and are not lethal to whole cell cultures, it may allow researchers to obtain long-term experimental results on cells affected by viruses.
This is the problem that we may encounter two types of cell pollution, chemical pollution and biological pollution, when we use cell culture consumables such as cell factories to cultivate cells.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English