July 06, 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration converted Leqembi (lecanemab-irmb), indicated to treat adult patients with Alzheimer’s Disease, to traditional approval following a determination that a confirmatory trial verified clinical benefit. Leqembi is the first amyloid beta-directed antibody to be converted from an accelerated approval to a traditional approval for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. The drug works by reducing amyloid plaques that form in the brain, a defining pathophysiological feature of the disease.
Leqembi was approved in January under the Accelerated Approval pathway. This pathway allows the FDA to approve drugs for serious conditions where there is an unmet medical need, based on clinical data demonstrating the drug’s effect on a surrogate endpoint—in the case of Leqembi, reducing amyloid plaques in the brain—that is reasonably likely to predict a clinical benefit to patients. As a postmarketing requirement of the accelerated approval, the FDA required the applicant to conduct a clinical trial, often referred to as a confirmatory study, to verify the anticipated clinical benefit of Leqembi. Efficacy of Leqembi was evaluated using the results of Study 301 (CLARITY AD), a Phase 3 randomized, controlled clinical trial.
“Today’s action is the first verification that a drug targeting the underlying disease process of Alzheimer’s disease has shown clinical benefit in this devastating disease,” said Teresa Buracchio, acting director of the Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “This confirmatory study verified that it is a safe and effective treatment for patients with Alzheimer’s disease.”
Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder affecting more than 6.5 million Americans. The disease slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and eventually, the ability to carry out simple tasks. While the specific causes of Alzheimer’s are not fully known, it is characterized by changes in the brain—including the formation of amyloid beta plaques and neurofibrillary, or tau, tangles—that result in loss of neurons and their connections.
Study 301 was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study that enrolled 1,795 patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Treatment was initiated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease and confirmed presence of amyloid beta pathology. Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive placebo or Leqembi at a dose of 10 milligrams (mg)/kilograms (kg), once every two weeks. Leqembi demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful reduction of decline from baseline to 18 months on the primary endpoint, the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale Sum of Boxes score, compared to placebo. Statistically significant differences between treatment groups were also demonstrated on all secondary endpoints, which included the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale Cognitive Subscale 14, and the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living Scale for Mild Cognitive Impairment.
On June 9, the FDA convened the Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee to discuss whether Study 301 provided evidence of clinical benefit of Leqembi for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. All committee members voted affirmatively that the results of the study verified the clinical benefit of Leqembi for the indicated use.
The most common side effects of Leqembi were headache, infusion-related reactions and amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA), a side effect known to occur with the class of antibodies targeting amyloid. ARIA most commonly presents as temporary swelling in areas of the brain seen on imaging studies that usually resolves over time and may be accompanied by small spots of bleeding in or on the surface of the brain. Although ARIA is often not associated with any symptoms, symptoms can occur and include headache, confusion, dizziness, vision changes and nausea. ARIA can also infrequently present with serious and life-threatening brain edema that can be associated with seizures and other severe neurological symptoms. Intracerebral hemorrhages can occur in patients treated with this class of medications and can be fatal. A boxed warning is included in the prescribing information to alert patients and caregivers to the potential risks associated with ARIA.
Source: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-converts-novel-alzheimers-disease-treatment-traditional-approval
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English

















































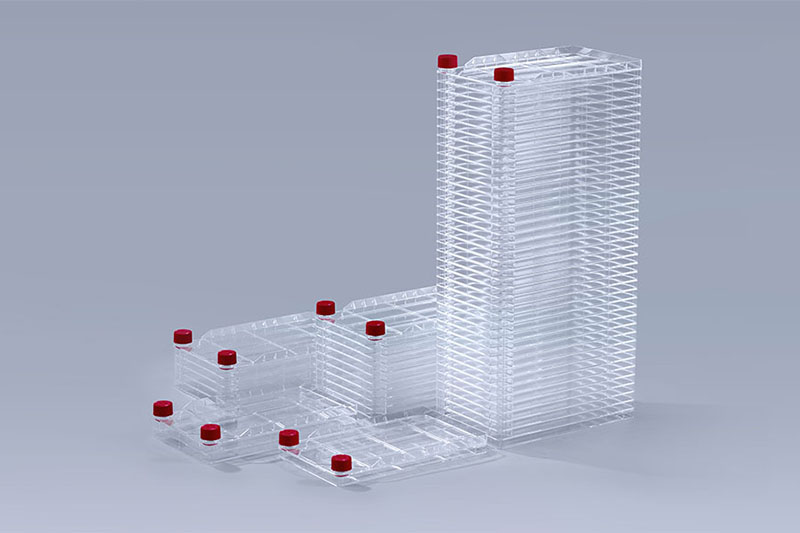 Cell Factory Systems
Cell Factory Systems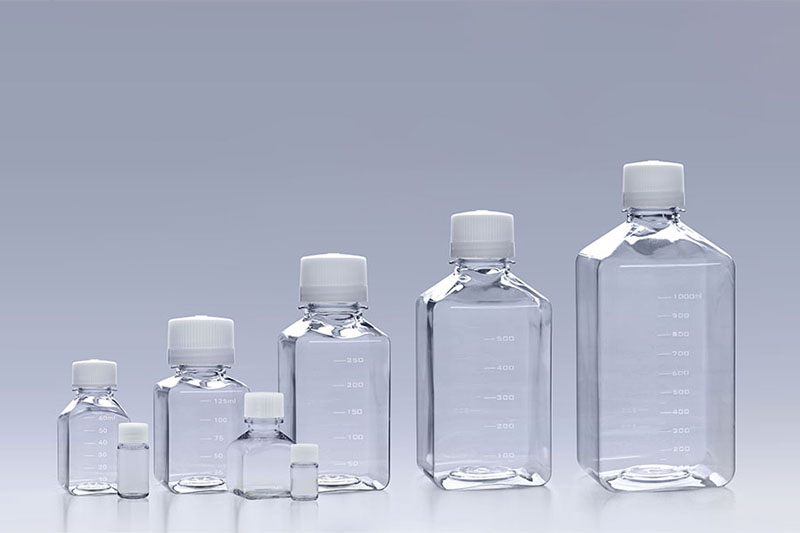 PETG Media Bottles
PETG Media Bottles