Cell factories are specialized culture vessels used for large-scale production of cells, such as mammalian or microbial cells, for various applications including biopharmaceutical production, vaccine development, and tissue engineering. While cell factories typically do not use caps in the traditional sense, as they are often equipped with specialized closures or systems to ensure a sterile and controlled environment, there are several components that play a crucial role in their operation. Here are some of the important components used in cell factories:
1.Sterile Filters: Cell factories require aeration and gas exchange while maintaining sterility. Sterile filters are essential components that are integrated into the design of cell factories. They allow the exchange of gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, while preventing the entry of contaminants. These filters are typically made of materials that provide both filtration and microbial retention capabilities.
2.Tubing and Connectors: Cell factories are typically connected to bioreactor systems or media supply systems through tubing and connectors. These components are designed to create a sealed connection, ensuring the integrity of the cell factory system. Various types of tubing and connectors are used depending on the specific requirements of the cell factory and the bioprocess being performed.
3.Sealing Systems: Cell factories are designed to be sealed to maintain sterile conditions within the culture vessel. Sealing systems can vary depending on the manufacturer and design of the cell factory. Examples include screw-top closures, gasket seals, or snap-fit locking mechanisms that securely hold the top and bottom halves of the cell factory together, ensuring a tight seal.
4.Sampling Ports: Cell factories often feature sampling ports that provide a convenient way to take samples from the culture without compromising the sterile environment. These ports are equipped with closures, such as septum seals or self-sealing membranes, to prevent contamination during sampling.
5.Harvesting Ports: In some cell factory designs, harvesting ports or sampling ports can also serve as outlets for cell collection or culture media removal. These ports may be equipped with specialized closures or connectors to allow for controlled cell harvesting or media draining.
6.Temperature and pH Probes: Monitoring and controlling temperature and pH are critical factors in cell culture processes. Cell factories often feature ports or access points for inserting temperature and pH probes. These ports may have closures or gaskets to maintain the integrity of the system while enabling regular monitoring.
It's important to note that the specific components and systems used in cell factories can vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended application. Always refer to the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for the proper use, assembly, and maintenance of the specific cell factory system you are working with.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English

















































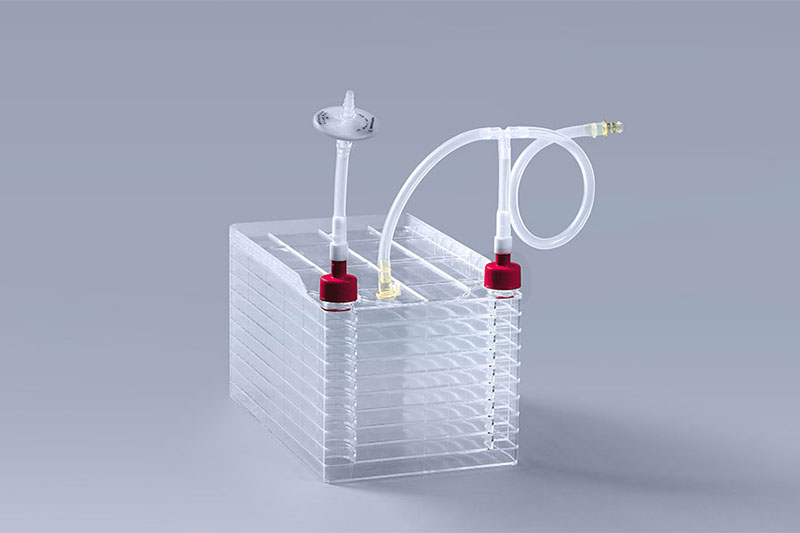 Cell Factory
Cell Factory