Cell culture technology plays a crucial role in biomedicine, bioengineering and other fields. In this process, cell factories, as an emerging cell culture vessel, are gradually becoming the mainstream choice for cell culture by virtue of their multi-layer structure and flexible specifications. In this paper, we will explore the different applications of cell factories and the advantages they bring.
Structure and specifications of cell factories
Cell factories are usually designed with multi-layer structures, with common specifications such as 1-layer, 2-layer, 5-layer, 10-layer and 40-layer. This design not only makes effective use of space, but also significantly improves the density and yield of cell culture, meets the needs of different scales and stages of cell culture, and improves the efficiency of laboratory work.
Application Areas
1 Biomedical
In the biomedical field, cell factories are widely used in drug development and production. By culturing cells in multilayer structures, biopharmaceuticals can be rapidly screened and produced, especially in the development of monoclonal antibodies, vaccines and cell therapy products. Its high-density culture capability greatly shortens the drug development cycle and improves production efficiency.
2 Agricultural Biotechnology
Cell factories also play an important role in agricultural biotechnology. By cultivating plant cells and tissues, high-yield planting materials can be obtained quickly. Especially when cultivating genetically modified plants and carrying out plant cell engineering, cell factories provide an ideal culture environment. This efficient cell culture method helps to promote sustainable agricultural production.
3 Industrial Biomanufacturing
Cell factories also have important applications in industrial biomanufacturing. Through metabolic engineering using microorganisms or cells, a variety of bio-based chemicals and fuels can be produced. The multi-layer design of cellular factories can improve reactor utilisation and enable efficient bioconversion processes, thereby reducing production costs.
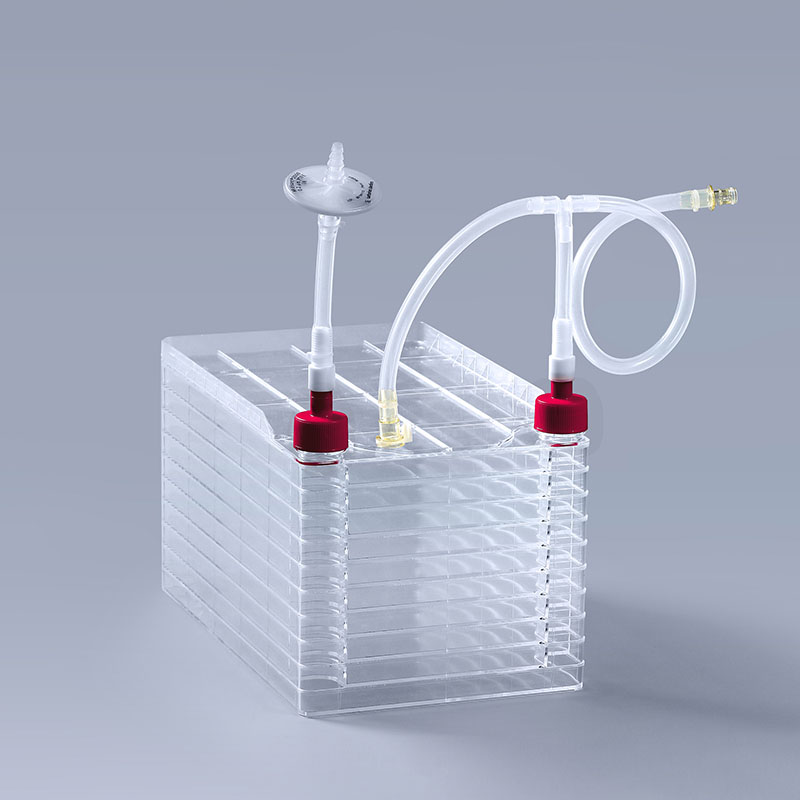

Advantage Analysis
1 High space utilisation
The multi-layer design of the cell factory allows more cells to be cultured per unit area, which greatly improves space utilisation and is particularly suitable for high-density cell culture.
2 Flexible operation
The independence of different layers allows users to flexibly adjust the culture conditions according to actual needs. This flexibility allows it to be adapted to different experimental designs and culture objectives.
3 Cost-effective
Due to the high throughput and high density of the cell factory, the cost of each experiment can be significantly reduced. At the same time, the shortened culture cycle reduces the consumption of resources and improves economic efficiency.
As an innovative cell culture vessel, the Cell Factory is changing the traditional way of cell culture with its multilayer structure and wide range of applications. Whether in biomedicine, agricultural biotechnology or industrial biomanufacturing, it shows great potential and advantages. With the continuous advancement of technology, cell factories will play a more important role in the future cell culture field, bringing more possibilities for scientific research and industrial production.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English