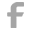The 5-layer cell factory, as an innovative cell culture container, has garnered widespread attention in the field of biomedicine due to its multi-layered structure and polystyrene material. As a medium-sized container, the 5-layer cell factory plays a crucial role in cell cultivation.
Multi-layered structure:
The standout feature of the 5-layer cell factory is its multi-layered structure. Each layer is interconnected through specially designed air vents and liquid conduits, creating a relatively independent and closely connected cultivation space. This design not only enhances the efficiency of cell culture but also allows for multiple experiments to be conducted in the same container, thus saving laboratory space and manpower costs.
Advantages in application:
The 5-layer cell factory is primarily used for adherent cell culture, catering to the cultivation needs of various cell types. Its large capacity design enables it to process multiple samples simultaneously, thereby increasing experiment throughput and efficiency. Furthermore, the polystyrene material boasts excellent transparency and biocompatibility, facilitating the observation of cell growth status and real-time monitoring of the cell culture process.
Potential challenges:
Despite its numerous advantages in cell culture, the 5-layer cell factory also faces some potential challenges. For instance, the multi-layered design may increase the complexity of operation and maintenance, necessitating careful control of each layer's cultivation conditions to ensure experiment stability and repeatability. Additionally, the large capacity design may lead to increased consumption of culture medium and difficulties in waste disposal, requiring proper planning and management.
In conclusion, the 5-layer cell factory, as an innovative cell culture container, holds vast application prospects in cell biology research and the field of biomedicine. By gaining a deeper understanding of its structural features, application advantages, and potential challenges, we can better leverage its role in cell cultivation, thereby driving the development and application of biotechnology.
The FAI climbed 5.9 percent year-on-year in the first 11 months of 2018, quickening from the 5.7-percent growth in Jan-Oct, the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said Friday in an online statement.
The key indicator of investment, dubbed a major growth driver, hit the bottom in August and has since started to rebound steadily.
In the face of emerging economic challenges home and abroad, China has stepped up efforts to stabilize investment, in particular rolling out measures to motivate private investors and channel funds into infrastructure.
Friday's data showed private investment, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total FAI, expanded by a brisk 8.7 percent.
NBS spokesperson Mao Shengyong said funds into weak economic links registered rapid increases as investment in environmental protection and agriculture jumped 42 percent and 12.5 percent respectively, much faster than the average.
In breakdown, investment in high-tech and equipment manufacturing remained vigorous with 16.1-percent and 11.6-percent increases respectively in the first 11 months. Infrastructure investment gained 3.7 percent, staying flat. Investment in property development rose 9.7 percent, also unchanged.
 English
English